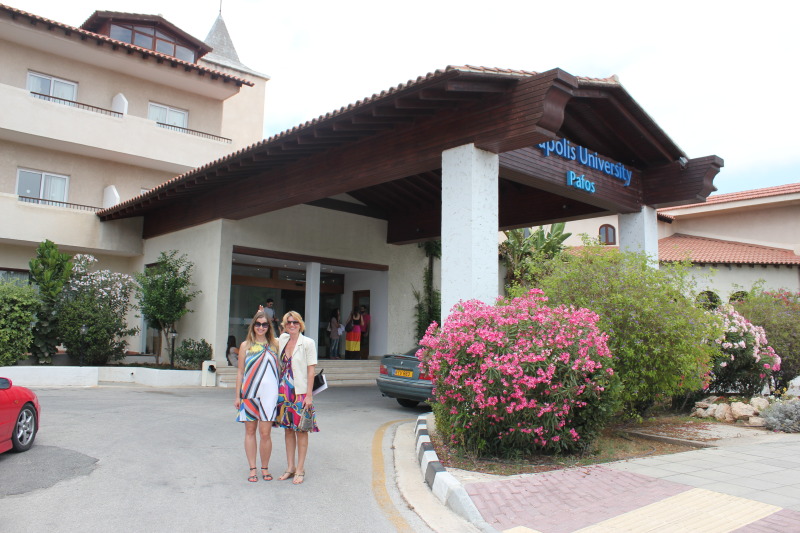
Neapolis University pafos ,Cyprus

Neapolis University pafos ,Cyprus
Paphos, CyprusAbout Us
The Neapolis University Pafos (NUP) is a private university in Paphos, Cyprus, that offers graduate and undergraduate degrees in Economic and Business Studies, Law, Health Sciences, Architecture & Land and Environmental Sciences,Theology and Greek Civilisation.
The university's academic programs focus on sectors that are critical to the Cyprus economy and are in high demand in the local job market. Real estate and construction along with the banking and financial sectors represent some of the most critical sectors not only for the Cyprus economy but also for the world economy, and, therefore, represent major focus of the university's undergraduate and post-graduate programmes.
The university offers undergraduate programmes in:
- Architecture and Environmental Design
- Real Estate Valuation and Development
- Business Administration
- Financial Studies
- Psychology
The university offers also post-graduate programmes in:
- Real Estate
- Construction Management
- Business Administration
- Banking, Investment and Finance
- Educational Psychology
Courses & Fees
Facilities

Library

Computer Services

Information Center
Accommodation Institution Hostel
| Room Type | Duration | Fee/Student |
|---|
Photos

neapolis@tenagents.com
News
Retailing during Covid-19: Weathering the storm
2022-02-11 00:00:00.000
<p>In addition to its tremendous effects on public health, COVID-19 has caused a major economic impact on every region, every industry, and ultimately on all aspects of human life</p> <p>by <strong>Antonios Zairis*</strong></p> <p>In addition to its tremendous effects on public health, COVID-19 has caused a major economic impact on every region, every industry, and ultimately on all aspects of human life. And what makes it even more difficult is that no one can predict neither the intensity nor the duration of the current situation. The financial crisis generated by Covid-19 is a global phenomenon, affecting every economy in the world, but with different intensity and dissimilar impact. Every country is experiencing economic consequences associated with demand and supply, but they are highly uneven across sectors and even between companies. The purchasing patterns and intentions of consumers were also modified (Eger et al., 2021; Grewal et al., 2021; Unnikrishnan and Figliozzi, 2021; Vazquez-Martinez et al., 2021).</p> <p>The paper focuses on the retail sector as it constitutes an economic heavyweight. It is usually the largest industry in a country’s economy in terms of turnover and employment. Among OECD countries 1 in 12 workers is employed in retail and almost 5% of GDP derives from the industry. It also has an important position in the value chains. Retail dominates the supply chain since it serves final demand, and works both as a household provider and as an outlet for upstream sectors. Moreover, it is a labour-intensive sector and therefore any difficulties it faces due to the current health crisis will also have a severe impact on the employment issue (OECD, 2020a). Counterweight to the crisis were the technological advances that had already reshaped the industry (Shankar et al., 2021).<br /> <br /> The study aims to provide an overview of the pandemic’s consequences on global retailing, the changes in consumer behaviour, and some emerging trends caused by the health crisis. It adds to the existing literature on the influence of COVID-19 by combining data and assessing its impact on the development of retail trade. This is followed by a description of the key factors that cause different effects in the industry. The final section contains the concluding remarks.</p>
Required Documents
| Document Name | File Name | File |
|---|